All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Acquired annuities come with a death advantage, which can give economic protection for your loved ones in the occasion of your fatality. If you are the recipient of an annuity, there are a few regulations you will certainly need to follow to acquire the account. First, you will require to supply the insurance company with a copy of the death certification for the annuitant.
Third, you will require to give the insurer with other called for paperwork, such as a copy of the will or trust. Fourth, depending on the type of inherited annuity and your personal tax obligation situation, you may require to pay tax obligations. When you acquire an annuity, you need to choose a payout alternative.
With an immediate payment alternative, you will begin obtaining payments right away. The repayments will be smaller sized than they would be with a postponed choice due to the fact that they will certainly be based on the present value of the annuity. With a deferred payout choice, you will not begin getting repayments later.
When you acquire an annuity, the taxes of the account will depend on the sort of annuity and the payment alternative you select. If you inherit a conventional annuity, the settlements you obtain will be strained as average revenue. If you inherit a Roth annuity, the repayments you receive will not be taxed.
Tax rules for inherited Variable Annuities
If you select a deferred payment alternative, you will not be taxed on the development of the annuity up until you begin taking withdrawals. Talking to a tax expert before acquiring an annuity is necessary to ensure you recognize the tax obligation implications. An acquired annuity can be a great method to give economic safety and security for your enjoyed ones.
You will certainly also require to comply with the guidelines for inheriting an annuity and choose the right payment alternative to suit your needs. Finally, make sure to talk to a tax obligation expert to ensure you understand the tax obligation effects of inheriting an annuity. An acquired annuity is an annuity that is passed down to a beneficiary upon the death of the annuitant
To acquire an annuity, you will certainly require to offer the insurance provider with a duplicate of the fatality certification for the annuitant and submit a beneficiary type. You may require to pay tax obligations depending on the kind of acquired annuity and your personal tax obligation scenario. There are two major kinds of acquired annuities: standard and Roth.

If you inherit a conventional annuity, the payments you receive will be strained as normal earnings. If you acquire a Roth annuity, the payments you receive will not be strained.
Are Immediate Annuities death benefits taxable
Just how an inherited annuity is taxed depends on a selection of factors, however one secret is whether the cash that's appearing of the annuity has actually been strained prior to (unless it remains in a Roth account). If the money dispersed from an annuity has not been strained previously, it will certainly be subject to tax obligation.

A certified annuity is one where the owner paid no tax obligation on payments, and it may be held in a tax-advantaged account such as conventional 401(k), typical 403(b) or traditional IRA. Each of these accounts is funded with pre-tax cash, implying that tax obligations have not been paid on it. Because these accounts are pre-tax accounts and earnings tax obligation has actually not been paid on any of the money neither payments neither profits circulations will certainly undergo ordinary income tax.
A nonqualified annuity is one that's been acquired with after-tax money, and circulations of any type of payment are not subject to revenue tax obligation since tax obligation has currently been paid on payments. Nonqualified annuities consist of 2 significant kinds, with the tax therapy depending on the kind: This type of annuity is purchased with after-tax cash money in a normal account.

Any kind of regular circulation from these accounts is complimentary of tax obligation on both contributed money and earnings. At the end of the year the annuity business will certainly file a Type 1099-R that shows exactly how much, if any, of that tax obligation year's distribution is taxed.
Beyond earnings taxes, an heir might additionally require to compute estate and estate tax. Whether an annuity undergoes revenue taxes is a totally different matter from whether the estate owes inheritance tax on its value or whether the beneficiary owes estate tax on an annuity. Estate tax is a tax analyzed on the estate itself.
The rates are dynamic and variety from 18 percent to 40 percent. Individual states might also impose an estate tax on money dispersed from an estate. On the other hand, inheritance taxes are tax obligations on an individual who gets an inheritance. They're not examined on the estate itself but on the heir when the properties are obtained.
Period Certain Annuities and inheritance tax
federal government does not evaluate estate tax, though six states do. Fees variety as high as 18 percent, though whether the inheritance is taxed depends on its dimension and your connection to the giver. Those acquiring big annuities should pay interest to whether they're subject to estate taxes and inheritance taxes, past simply the standard earnings tax obligations.
Beneficiaries ought to take notice of potential inheritance and estate tax obligations, too.
It's an agreement where the annuitant pays a swelling amount or a series of premiums in exchange for a guaranteed earnings stream in the future. What happens to an annuity after the proprietor passes away hinges on the particular details described in the agreement.
Other annuities provide a fatality benefit. The payout can take the kind of either the whole continuing to be balance in the annuity or a guaranteed minimum amount, normally whichever is better.
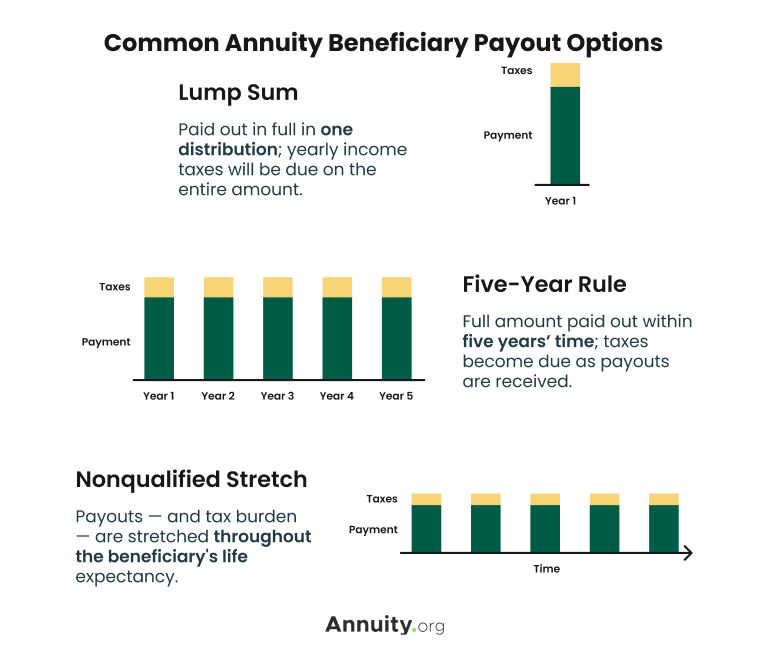
It will plainly recognize the recipient and potentially detail the offered payment options for the death benefit. An annuity's fatality advantage guarantees a payment to a marked recipient after the owner passes away.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Understanding Immediate Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Everything You Need to Know About Fixed Vs Variable Annuities What Is Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity? Features of Fixed Vs Variable Annuiti
Highlighting Pros And Cons Of Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity Key Insights on Annuities Variable Vs Fixed Defining What Is Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Pros and Cons of Various Financial Optio
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments A Comprehensive Guide to Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuities What Is What Is Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity? Pros and Cons of Pros And C
More
Latest Posts